Get notes, summary, questions and answers, MCQs, extras, and PDFs of Chapter 1 “Earth As a Planet” which is part of ICSE Class 9 Geography (Morning Star) textbook/workbook answers. However, the notes should only be treated as references and changes should be made according to the needs of the students.
If you notice any errors in the notes, please mention them in the comments
Summary
Chapter 1 discusses Earth as a planet and its unique characteristics. Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only one known to support life. From space, it appears blue due to the abundance of water, covering 70% of its surface. Earth is part of the solar system, which consists of the Sun and other celestial bodies like planets, satellites, asteroids, and comets.
The chapter explains how Earth’s shape was proven to be spherical over time. Observing a ship from a distance at sea, only its mast is visible first, and then the rest of the ship, proving Earth’s curved surface. This idea is supported by other evidence, such as the Bedford Level Experiment, lunar eclipses, the appearance of the Pole Star, satellite images, and the fact that sunrise and sunset happen at different times across the globe.
Though Earth is described as spherical, it is slightly flattened at the poles and bulges at the equator due to its rotation. This shape is called an oblate spheroid. Earth’s size at the equator is larger compared to its size at the poles.
Earth is the only known planet to support life because of its optimal distance from the Sun, suitable temperature, presence of an atmosphere, and availability of water. These features make Earth habitable, with the atmosphere providing gases essential for life and protecting it from harmful solar radiation. The planet’s water cycle plays a significant role in maintaining a stable climate and supporting life across its surface.
Also, the chapter introduces the biosphere, a zone where all life exists, and how various life cycles, such as the carbon and oxygen cycles, help maintain the balance needed for life on Earth.

Video tutorial
Textbook solutions
Multiple-Choice Questions
1. At the Bedford level canal area a famous experiment was carried out. How many poles were used and at what distance apart?
(a) 3 poles, 5km
(b) 2 poles, 10km
(c) 4 poles, 5km
(d) 3 poles, 10km
Answer: A. 3 poles, 5km
2. The view of the earth’s surface as seen from a height is
(a) square
(b) rectangular
(c) circular
(d) triangular
Answer: C. circular
3. At what angle can the Pole Star be seen at the Poles and at the Equator?
(a) 60°, 30°
(b) 90°, 0°
(c) 45°, 45°
(d) 0°, 90°
Answer: B. 90°, 0°
4. Magellan’s ship Victoria after completing a round-the-world voyage in 1522 returned to which country?
(a) France
(b) Spain
(c) London
(d) United States of America
Answer: B. Spain
5. Earth’s diameter at the Equator is _______ and at the poles is _______.
(a) 12,750 km, 12,715 km
(b) 12,752 km, 12,726 km
(c) 12,714 km, 12,755 km
(d) 12,756 km, 12,714 km
Answer: D. 12,756 km, 12,714 km
6. What is the shape of the earth?
(a) Sphere
(b) Oblate
(c) Geoid
(d) Spheroid
Answer: B. Oblate
7. What is the shape of earth called?
(a) Oblate
(b) Spherical
(c) Oval
(d) Oblate Spheroid
Answer: D. Oblate Spheroid
8. The atmosphere of Venus has maximum concentration of which gas?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Helium
Answer: B. Carbon dioxide
9. Name the gas that absorbs the harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun.
(a) Ozone
(b) Oxygen
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Nitrogen
Answer: A. Ozone
10. What is the thickness of the Biosphere?
(a) 20 km
(b) 19 km
(c) 15 km
(d) 25 km
Answer: C. 15 km
11. What term refers to a self-regulating and self-sustaining unit of the biosphere?
(a) Ecosystem
(b) Food cycle
(c) Biome
(d) Ecology
Answer: A. Ecosystem
12. Name the cycle through which solar energy moves from non-living to living organisms and back.
(a) Carbon cycle
(b) Nitrogen cycle
(c) Nutrition cycle
(d) Energy cycle
Answer: A. Carbon cycle
13. Name the basic raw material for life.
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Carbon
(c) Oxygen
(d) Solar energy
Answer: B. Carbon
14. Name the genius mathematician astronomer from the ancient world who was the first proponent of the round shape of the earth.
(a) Pythagoras
(b) Aryabhatta
(c) Brahmagupta
(d) Bhaskara
Answer: B. Aryabhatta
15. You are standing at a beach looking towards the horizon. You hear the horn of a ship. Which part of the ship will you see first?
(a) Hull
(b) Deck
(c) Mast
(d) All of them
Answer: C. Mast
16. Where was the Bedford Level Experiment carried out?
(a) England
(b) France
(c) India
(d) Canada
Answer: A. England
Short Answer Questions
1. How can you prove that the earth is a sphere by looking at the horizon?
Answer: The view of the earth’s surface as seen from a height is circular. With increase in altitude, the circular horizon also widens. Had the earth’s surface been flat, the horizon would have been the same irrespective of altitude.
2. Briefly describe the shape of the earth.
Answer: The earth is said to be spherical; but it is not a perfect sphere. Its diameter varies at the Equator and at the Poles. This difference in diameter is due to the centrifugal force of the earth’s rotation at a great speed which forms a bulge at the Equator and a compression at the Poles. Thus, the earth is said to be an Oblate Spheroid. The shape of the earth is also described as Geoid, which means earth-shaped.
3. What is the earth’s mean temperature? State its one advantage.
Answer: The earth has an average temperature of 17°C which is suitable for life to exist.
4. Why is the earth called a watery planet?
Answer: Earth is called a watery planet because 70 per cent of its total area is covered by water.
5. What is ‘biosphere’?
Answer: Biosphere is the narrow realm of contact and interaction between the atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere. It provides all the necessities for all the species living on earth, i.e., light, heat, water, food and habitats. Biosphere is a thin layer of approximately 15 km from the deepest ocean trench to the highest mountain peak. It is the life zone of the earth.
6. Name the conditions necessary for life on earth.
Answer:
- Distance from the Sun: The earth is at an optimum distance from the sun, hence it is neither too hot nor too cold.
- Temperature: The earth has an average temperature of 17°C, which is suitable for life to exist.
- Atmosphere: The earth’s atmosphere contains life-supporting gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Ozone in the atmosphere absorbs harmful ultraviolet rays.
- Water: The earth has 70 per cent of its surface covered by water, which moderates the climate and surface condition of the earth.
- Solid Crust (Lithosphere): Earth has a solid crust that provides soil for plant life, which supports all forms of life.
7. Give any two features of the earth that make it a ‘Unique Planet’.
Answer:
- Earth is the only planet that supports life. Unlike other planets, it is covered with green vegetation, enormous blue-green oceans containing over a million islands, and a large number of streams and rivers.
- The earth has certain features that make it habitable, such as its atmosphere, distance from the sun, and availability of water.
8. What would happen if the average temperature of the earth increased by half a degree?
Answer: If the average temperature on the earth’s surface changes by only a few degrees, many species would perish due to extreme heat or cold.
9. Trace the cyclical movement of carbon in the three realms of the earth.
Answer: Carbon is the basic raw material of all life. Atmospheric carbon dioxide is used by plants in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll to make their own food by the process of photosynthesis. From the plants, carbon moves along the food chain through consumers at different levels. After the death of plants and animals, the carbon present in their bodies is decomposed and absorbed as food by saprophytic bacteria and fungi. When plants die and get buried in the soil, they undergo slow degradation and compaction. This results in the formation of fossil fuels containing huge amounts of carbon. During respiration, plants, animals, and humans use atmospheric oxygen and release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. The burning of carbon-containing fuels also results in the release of CO2 into the atmosphere. Thus, carbon from CO2 taken by green plants from the environment through photosynthesis is returned to the environment through respiration, decomposition, and through the burning of fuels.
Structured Questions
1. (a) How does the sighting of a ship from the seashore prove that the earth is round in shape?
Answer: While standing at the seashore, watching an approaching ship, we first see only its mast. Then, as it comes closer, we can see the deck in the middle, then its funnel, and finally the hull comes into full view. This can happen only when the earth’s surface is curved. If the earth were flat, the entire ship would have been visible at once.
(b) Use a 1m long table to replicate the Bedford Level Experiment. Briefly mention how did you carry out the experiment to prove the shape of the earth.
Answer: Do it yourself.
The Bedford Level Experiment can be replicated by placing three poles of equal length at intervals of 5 cm on a 1m long table. These poles should be positioned such that they are of the same height above the table. When viewed from one end of the table, the middle pole will appear slightly higher than the others. This demonstrates that the surface is curved, similar to how the Bedford Level Experiment proved that the earth’s surface is curved.
(c) Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) The sunrise and sunset occur at different times at different places.
Answer: Sunrise and sunset occur at different times at different places because the earth rotates from west to east. Therefore, people in the east can see the sun earlier than those in the west.
(ii) The earth is not a perfect sphere.
Answer: The earth is not a perfect sphere because it bulges slightly at the Equator and is flattened at the Poles due to the centrifugal force of the earth’s rotation.
(iii) Venus is hotter than Mercury.
Answer: Venus is hotter than Mercury because the atmosphere around Venus is mainly composed of carbon dioxide, which produces a greenhouse effect on the surface of Venus, causing its temperature to remain very high.
(d) Draw a well-labelled diagram to show that the horizon of the earth is circular in shape.
Answer: The higher the altitude, the wider the circular horizon. The circular horizon AB widens to CD as you move up from Y to X.
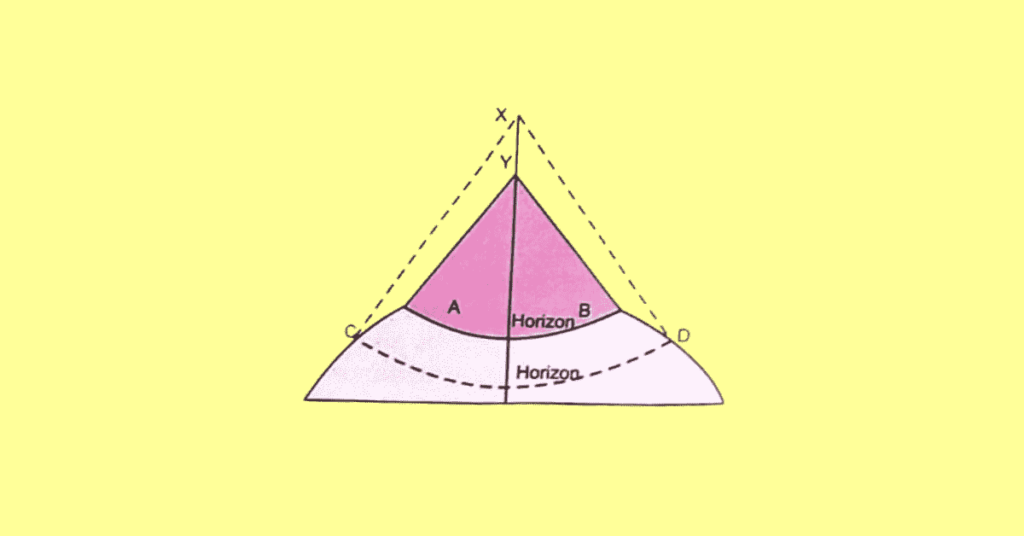
2. Describe the role of each of the following in making earth a habitable planet.
(a) Atmosphere
Answer: The earth’s atmosphere is made up of life-supporting gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. The ozone present in the atmosphere absorbs harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun and prevents loss of heat from the earth’s surface, helping to keep the earth warm.
(b) Water
Answer: Water plays a crucial role in making the earth habitable as 70 per cent of the earth’s surface is covered by water. Water bodies absorb a large amount of heat during the day and release it slowly at night, thus moderating temperature and making the climate conducive to life.
(c) Temperature
Answer: The earth has an average temperature of 17°C, which is suitable for life to exist. A slight change in temperature would result in extreme heat or cold, making it difficult for many species to survive.
(d) Distance from the Sun
Answer: The earth is at an optimum distance from the sun, making it neither too hot nor too cold. This distance allows life to thrive, as it ensures that the earth receives the right amount of heat and light from the sun.
3. (a) How does each of the following prove the circular shape of the earth:
(i) Lunar Eclipse
Answer: The shadow of the earth on the surface of the moon is clearly visible from the earth during a lunar eclipse. It appears as an arc of a circle, which can only happen if the earth is spherical.
(ii) Pole Star
Answer: The Pole Star can be seen at an angle of 90° at the North Pole and its angle decreases towards the Equator. At the Equator, the angle is 0°. This can happen only in an arc of a circle.
(b) What is an ecosystem? Give an example.
Answer: The self-regulating and self-sustaining structural and functional unit of the biosphere is called an ecosystem. This system depends upon the sun for its energy. A pond, a lake, a desert, grassland, meadow, and forests are common examples of ecosystems.
(c) Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Earth is a habitable planet.
Answer: Earth is a habitable planet because it has an atmosphere that supports life, moderate temperatures, water, and an optimal distance from the sun.
(ii) From space Earth looks blue.
Answer: From space, the earth looks blue because 70 per cent of its surface is covered by water.
(iii) Water bodies reduce the day-night temperature variations.
Answer: Water bodies absorb heat during the day and release it at night, thus moderating temperature variations between day and night.
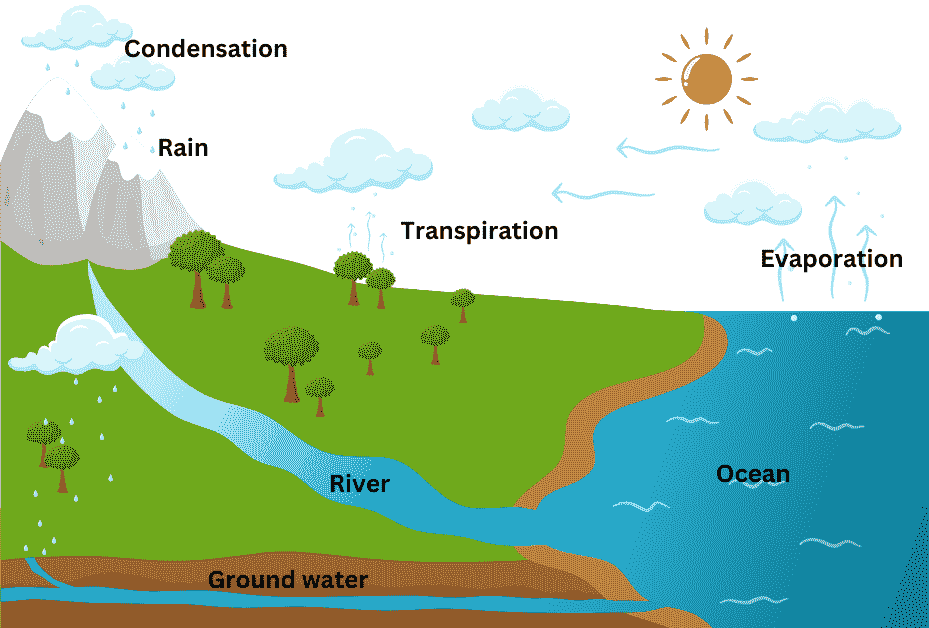
(d) Draw a well-labelled diagram to show the cyclic circulation of water between the three realms of the earth.
Answer:
Thinking Skills
1. You have gone from Delhi to Arunachal Pradesh on a study tour with your school during the winter vacation. As you woke up in the morning at 6 o’clock, you noticed the sun has risen whereas at Delhi sun rise is around 7.30 a.m. Similarly around 4.30 it was sunset while sunset is around 6 p.m. in Delhi. What do you think could be the reason for the sun rising and setting earlier than Delhi? Which feature of the earth can you relate to from this?
Answer: The reason for the sun rising and setting earlier in Arunachal Pradesh than in Delhi is due to the earth’s rotation from west to east. Arunachal Pradesh is located to the east of Delhi, and therefore, it experiences sunrise and sunset earlier. This is related to the rotation of the earth, which causes different places to experience sunrise and sunset at different times.
2. The earth depends upon the sun for its energy. Imagine a day, when the sun would not rise. Write down the consequences for the earth and its inhabitants.
Answer: If the sun would not rise, the earth would face several drastic consequences. There would be no sunlight, which would result in darkness. Plants would not be able to perform photosynthesis, leading to a collapse of the food chain. The temperature on earth would drop, making it extremely cold. Without the sun’s energy, life on earth would not be able to sustain, and eventually, all living organisms would perish due to lack of light and heat.
Extras
Additional MCQs
1. What percentage of the Earth’s surface is covered by water?
A. 50%
B. 60%
C. 70%
D. 80%
Answer: C. 70%
52. What is released back into the atmosphere by green plants during photosynthesis?
A. Nitrogen
B. Hydrogen
C. Carbon dioxide
D. Oxygen
Answer: D. Oxygen
Additional Questions and Answers
1. Which planet is the third from the Sun?
Answer: Earth.
70. What is the hydrological cycle, and how does it contribute to life on Earth?
Answer: The hydrological cycle, also known as the water cycle, is the continuous movement of water between the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere. It begins with the evaporation of water from seas, rivers, lakes, and other water bodies into the atmosphere, where it condenses to form clouds. This condensed water then falls back to the Earth’s surface as precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, or hail). Once on the ground, the water either infiltrates into the soil to become groundwater or flows back into rivers, lakes, and oceans, completing the cycle. This cycle is essential for life on Earth as it regulates the distribution of water, ensures a constant supply of fresh water, and maintains the balance of ecosystems by supporting plant growth and providing habitats for various species. Without the hydrological cycle, life on Earth would not be possible.

Get notes of other boards, classes, and subjects
