Get notes, summary, questions and answers, MCQs, extras, and PDFs of Chapter 18 “Energy” which is part of NBSE Class 11 Environment Education. However, the notes should only be treated as references and changes should be made according to the needs of the students.
If you notice any errors in the notes, please mention them in the comments
Summary
The chapter on energy begins by defining energy as the capacity to do work. It highlights that energy is essential for various activities such as cooking, transportation, and powering machinery. Different forms of energy are discussed, including potential, kinetic, thermal, chemical, electrical, and nuclear energy. It explains how energy can be converted from one form to another, like converting chemical energy from coal into thermal energy when it burns.
Historically, humans started using fire for cooking and protection. Over time, they learned to harness energy from coal, wind, water, and petroleum. The Industrial Revolution, sparked by the invention of the steam engine, led to a massive increase in energy consumption. Today, energy is crucial for running industries, cities, and modern agriculture, which relies on machinery, irrigation systems, and transportation. As societies became industrialized, energy use increased rapidly, especially in developed countries.
The chapter compares energy consumption between developed and developing countries. Although 80% of the world’s population lives in developing countries, they use only 30% of global energy. The text emphasizes that energy consumption is closely linked to the quality of life, as richer nations consume more energy per person.
In India, rising energy demand is attributed to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changes in lifestyle. However, India struggles to meet its energy needs, relying on imports for crude oil. Inefficiency in power generation and transmission further worsens the energy shortage. The gap between demand and supply is growing, leading to power outages and increased pressure on resources like firewood and coal.
Textbook solutions
Multiple-Choice Questions
1. Energy stored in a body because of its position or shape is called
(a) Kinetic Energy
(b) Chemical Energy
(c) Potential Energy
(d) Nuclear Energy
Answer: c. Potential Energy
2. 1 exajoule is equal to
(a) 10¹⁷ joules
(b) 10⁸ joules
(c) 10¹⁰ joules
(d) 10¹⁸ joules
Answer: d. 10¹⁸ joules
3. Where does the 67% of energy lost in a nuclear power plant?
(a) Water cooling system
(b) Combating radioactivity
(c) Converting nuclear energy into kinetic energy
(d) Heat loss
Answer: a. Water cooling system
4. 10¹⁵ Btu is equal to
(a) 1 Quad
(b) 1 joule
(c) 1 Terawatt-year
(d) All of these
Answer: a. 1 Quad
5. Naturally occurring, unrefined petroleum product composed of hydrocarbon deposits and other organic materials is
(a) Vaseline
(b) Crude oil
(c) Gasoline
(d) Natural Gas
Answer: b. Crude oil
Short Answer Questions
1. What is thermal energy?
Answer: Thermal energy is the energy associated with heat.
2. What is nuclear energy?
Answer: Nuclear energy is the energy contained in the nucleus of an atom, which binds the subatomic particles together. This energy can be released in the form of heat or light energy, either by fission or fusion.
3. How was fire used by early humans?
Answer: Early humans used fire for cooking food, keeping themselves warm, and for protection against wild animals. Later, they began to use fire to extract metals from their ores and make tools.
4. Why is energy consumption in India rising?
Answer: Energy consumption in India is rising because of rapid industrialisation, urbanisation, mechanisation, economic growth, population growth, and changing lifestyles and aspirations of the people.
5. How is energy used in our homes? Give examples.
Answer: Energy is used in our homes for lighting, heating water, running fans, coolers, air conditioners, radio, television, mixers, grinders, etc. A large quantity of fuel is also consumed by the means of transport.
6. Why is natural gas projected to be the fastest growing primary energy resource?
Answer: Natural gas is projected to be the fastest growing primary energy source worldwide, maintaining growth of 3.2 per cent annually over the 1999-2020 period, more than twice as high as the rate for coal. Natural gas consumption is projected to rise primarily for electricity generation. Gas is increasingly being seen as the desired alternative for electric power, given the efficiency of combined-cycle gas turbines relative to coal or oil-fired generation, and because it burns more cleanly than either coal or oil, making it a more attractive choice for countries interested in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Long Answer Questions
1. Trace the use of energy from ancient to modern times.
Answer: About 400,000 years ago, early humans discovered a source of energy—fire. They used fire for cooking food, keeping themselves warm and for protection against wild animals. Later, they began to use fire to extract metals from their ores and make tools. With the help of tools, they began to practise agriculture. They also tamed animals to harness their muscle power for agricultural tasks.
Later on, humans started harnessing the energy of coal, wind, water and petroleum. The invention of the steam engine led to the Industrial Revolution. Many industries were set up, which led to rapid industrialisation in Europe and the United States. With the development of various industries during the last century, the demand for energy increased very rapidly. Modern man uses about one hundred times more energy than early humans.
Energy consumption is increasing due to the setting up of new industries and the growth of cities. Energy consumption is also very large in modern agriculture due to the use of machinery, fertilisers, insecticides, and water supply from wells and canals. The storage of foodgrains and transportation also consumes energy.
During the hunter-gatherer stage of civilisation, the total energy required by one man was 2000-4000 kilocalories per day, obtained entirely through the food chain. Later, he discovered fire and used wood as fuel for cooking and warmth, leading to a gradual increase in per capita fuel consumption. The 19th-century industrial societies used fossil fuels, and the daily per capita energy utilisation went up to 70,000 kcal for industry, transport, communication, comfort, etc. An average American now uses 2,50,000 kilocalories per day.
2. Explain through a graph the relationship between income and the type of fuel used.
Answer: A strong relationship exists between income and the type of fuel used. As income increases, people tend to use higher quality fuels that are more energy efficient, cleaner, and easier to use. The progression of fuel use is depicted in the following energy ladder:
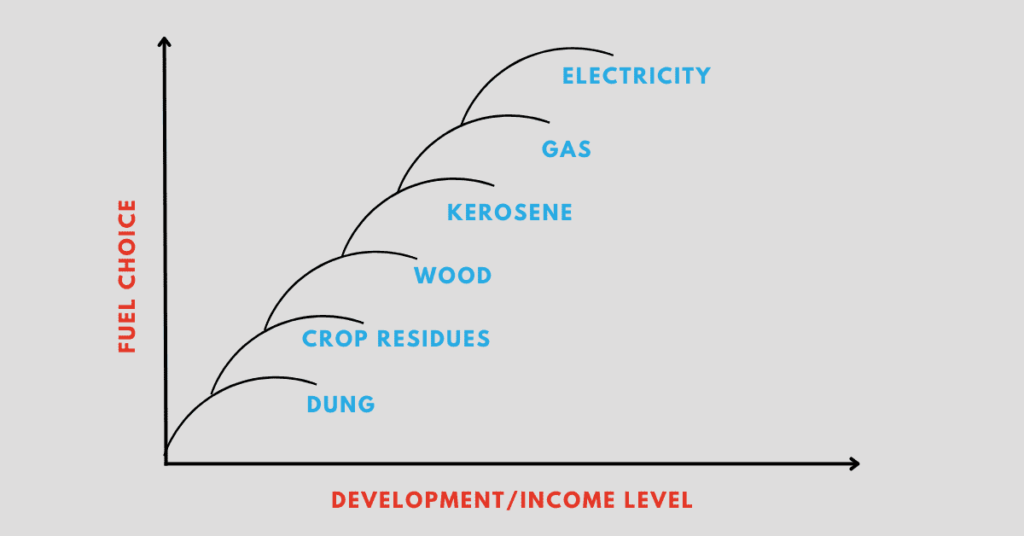
Energy Ladder:
- Electricity
- Gas
- Kerosene
- Wood
- Crop residues
- Dung
As people progress in terms of income and development, they move from using solid fuels like wood, crop residues, and dung to liquid fuels like kerosene, and eventually to gas and electricity.
3. What is the cause of energy shortage in our country?
Answer: The causes of energy shortage in India are as follows:
- The supply of energy has not been able to keep pace with the rising demand.
- There are shortages of petrol, cooking gas, electricity, kerosene, and firewood in everyday life.
- There is a large gap between India’s demand and supply of two major forms of commercial energy, namely electricity and coal.
- Over the last decade, shortages of coal and electricity have worsened. On a countrywide basis, the gap is about 10 per cent less than the potential demand.
- Widespread inefficiency in power generation, transmission, management, and use increases energy shortage.
- Power plants use obsolete equipment and processes. Poor maintenance of equipment and inadequate monitoring procedures are also causes of inefficiency.
- More than 20 per cent of the electricity generated in India is lost during transmission and distribution. These losses occur due to many transformation stages, poor-quality wires, equipment friction, and heat loss.
4. What are differences in energy consumption in rural and urban regions?
Answer:
| In Rural Regions | In Urban Regions |
|---|---|
| 1. The fossil fuel is used which causes pollution. | 1. Electrical energy and LPG for cooking is used. |
| 2. Most of the household equipment causes pollution, leading to ill health. | 2. People use electrical gadgets and appliances, which do not produce pollution. |
| 3. Life is slower as domestic animals are used for means of transport. | 3. People use electric trains, cars, buses, etc., to perform daily activities quickly. |
| 4. Since the people have low income, they cannot afford a high cost of living. | 4. In modern developed cities, economically advanced people have the comforts and luxuries which consume more energy. |
5. Why is crude oil production in our country not enough to meet the demands of petroleum products?
Answer: India’s crude oil production is not enough to meet the growing demand for petroleum products because:
- India’s production of crude oil in 2000-2001 was only 33 million metric tonnes (MMT), which is just about 35 per cent of the country’s annual requirement.
- There is a huge gap between the consumption and production of crude oil, petrol, and other petroleum products.
- This gap is filled through imports. The consumption of petroleum products is increasing at a high rate.
- A major amount of the country’s foreign exchange is used for the import of crude oil.
Think and Answer
1. Has energy contributed to the quality of life? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer: Yes, energy has contributed to the quality of life. It is essential for all activities on Earth and plays a significant role in various sectors such as agriculture, transportation, and industries. The use of energy enables us to grow food, cook it, and keep ourselves warm or cool. It is also used in transportation and powering industries, which directly impacts the quality of life. The shift to more efficient and cleaner forms of energy, such as electricity and natural gas, improves living conditions, reduces pollution, and enhances comfort and convenience. The consumption of energy in homes for lighting, heating, and using appliances like air conditioners, fans, and mixers also shows how energy has become integral to modern life. Thus, access to energy is closely linked to the quality of life, and as energy use increases, so do the standards of living.
2. Mohit thinks that India can become a developed country only if it uses more and more energy. Rohit thinks Mohit is wrong in thinking so. Who is right? Why?
Answer: Rohit is right. While energy consumption is important for development, simply using more and more energy does not necessarily lead to a country becoming developed. It is essential to focus on the efficient use of energy, sustainable energy sources, and reducing wastage. Increasing energy consumption without improving efficiency can lead to higher costs, pollution, and depletion of resources. Therefore, development is not just about increasing energy usage but also about using it wisely and sustainably.
Extras MCQs
1. What is the capacity to do work known as?
A. Power
B. Force
C. Energy
D. Momentum
Answer: C. Energy
16. How many times more commercial energy does an American use compared to an Indian?
A. 10 times
B. 15 times
C. 20 times
D. 24 times
Answer: D. 24 times
Extra Questions and Answers
1. What is energy?
Answer: Energy is the capacity to do work. It is an essential requirement for all activities on Earth. Energy is used to grow food, to cook it, to keep us warm or cool, to move us from one place to another, and for many other purposes.
24. How has the global pattern of energy consumption changed over time?
Answer: Global energy consumption patterns have changed significantly over time. Initially, early humans relied solely on energy obtained through the food chain, requiring about 2000-4000 kilocalories per day. With the discovery of fire, the use of wood as fuel increased, leading to a gradual rise in per capita fuel consumption. The Industrial Revolution in the 19th century saw the widespread use of fossil fuels, with daily per capita energy utilisation reaching 70,000 kilocalories for industry, transport, and communication. In modern times, the energy consumption of an average American has escalated to 250,000 kilocalories per day. The increasing energy demands are driven by industrialisation, urbanisation, and the growing need for transportation, food storage, and modern conveniences.
Get notes of other classes and subjects
| NBSE | SEBA/AHSEC |
| NCERT | TBSE |
| WBBSE/WHCHSE | ICSE/ISC |
| BSEM/COHSEM | MBOSE |
| Share Feedback | Question Papers |


